During last GUADEC, I had a chance to briefly present my project of having a powerful yet simple video game manager and player for GNOME. To make it a reality, a lot of work was needed on the backend side.
This article present the release of the first version of this backend, in its release candidate form.
Libretro
Libretro is a C/C++ API used mainly by retro video game console emulators and game engines. Writing an emulator and writing a GUI application require very different skills, using Libretro allows to isolate the backends (often called modules or cores) implementing the API from the frontends using the API to manipulate them, easying the port of the emulators or engines and offering a multiplicity of cores to choose from to application developers.

The main frontend of Libretro is RetroArch and it have been ported across multiple systems.
Retro
Retro (or retro-gobject) is a GObject based Libretro wrapping library written in Vala. It eases the creation of Libretro frontends by using OOP and automatic memory management (thanks to Vala and GObject); it allows the creation of Libretro frontends in other languages than C/C++ via GObject Introspection; and it allows to have multiple Libretro cores loaded at the same time, through the use of a global variable to store the calling core’s identity, and through file copy to avoid global variable collision in already used modules). Retro’s API is not to be considered stable yet, but it is very close to be and shouldn’t change much. Some objects are marked with a temporary internal visibility until they are tested and polished and can be part of the public API.
But most importantly, what Retro isn’t is a fork of Libretro. All it does is to wrap it in a nice object-oriented layer and it is fully compatible with modules implementing Libretro.
Retro’s git repository can be found here: https://github.com/Kekun/retro-gobject
Retro version 0.1 RC can be found here: https://github.com/Kekun/retro-gobject/releases/tag/v0.1-rc
Core
Core is the most important class of Retro. It represents the functionalities associated to a Libretro module and allow you to run it. A Core allows you to get information about its module, to set interfaces to handle the module’s callbacks, and most importantly, to run it.
Video
The Video interface is use by a Core to ask the frontend to render video and to set details about how the video must be rendered, such as the source video’s pixel format.
Audio
The Audio interface is used by a Core to ask the frontend to play audio.
Input
The Input interface is used by a Core to ask the frontend about the state of the input devices, such as gamepads, keyboards and mice.
Other interfaces
Lots of other interfaces can be set by the frontend or by the Core to communicate. Some examples are the Log interface, to let the Core write log messages, to the standard output or a file by example; the DiskControl interface, to let the frontend control a Core’s virtual disk drive (for example, to swap disks on a CD based game console emulator); or the Variables interface to allow the frontend to know about the Core’s special options and to set them.
RetroGtk
RetroGtk is a library written in Vala which links Retro, in order to run Libretro modules, and Gtk. It offers Gtk widgets implementing various Retro interfaces, allowing to easily display a Core’s video, to forward keyboard and mouse events to it, and to mimick gamepads with a keyboard.
RetroGtk also contains non-Gtk related objects, like loops to help running a Core, an interface to forward a Core’s log to a FileStream, and an interface to help manage a Core’s variables.
You can use Clutter and ClutterGtk or Cairo to render the video, and I hope that the inclusion of a Gl widget in Gtk+ 3.16 will allow to get rid the dependency on Clutter. It currently can also play a Core’s audio via PulseAudio, but it may be moved to some “RetroPa” library. Proper joystick support is still to come, certainly in a separate library (RetroJs?). RetroGtk’s git repository can be found here: https://github.com/Kekun/retro-gtk
Libretro module collection
Being able to run, control and render Libretro implementations is of no use if you have no such implementation to run, control and render. To help solving this, I started collecting GPL compatible implementation in a git repository, adding a makefile to ease the compiling and installing them. It is still in its infancy but it already helped me quite a lot.
The machines currently emulated by the collection are:
- Nintendo Entertainment System
- Super Nintendo Entertainment System
- Game Boy Advance
- Saturn
- PC Engine
- DOS
PlayStation support is to come, but an annoying bug in the emulator have to be solved first.
You can find this collection here: https://github.com/Kekun/libretro-free
Applications
Demo
To test all of this, I wrote a demo application, which uses Retro, RetroGtk and the module collection to run games. It allows you to open several game files (see the modules in the collection to know what can be run), to set the Core’s options, and it supports inputs such as the keyboard, the mouse, and can use the keyboard as a virtual gamepad. You can set the virtual gamepad’s configuration via a button.
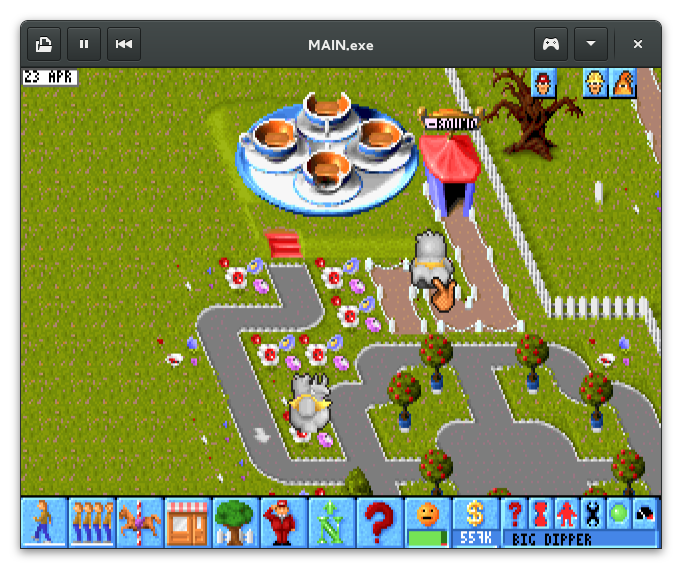
Theme Park running in DOSBox
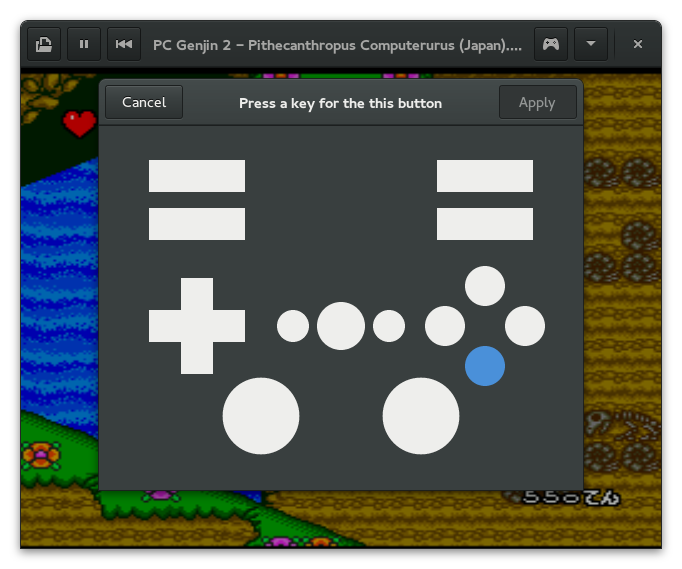
Virtual gamepad configuration when running PC Genjin 2 in Mednafen
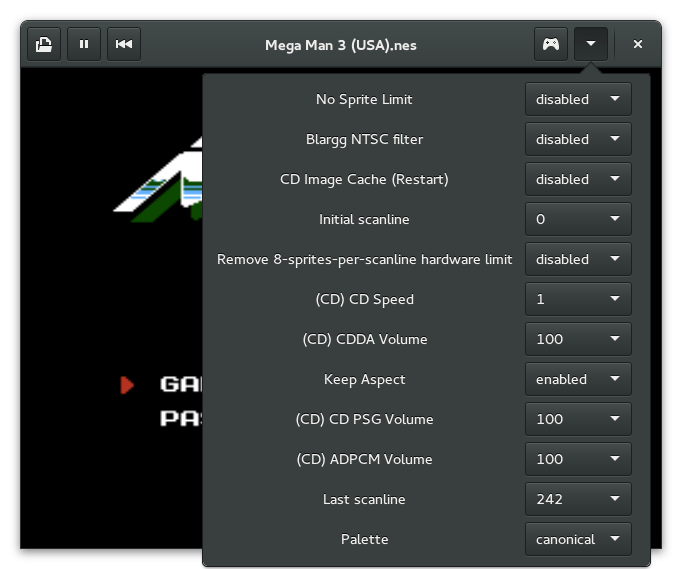
Nestopia’s options
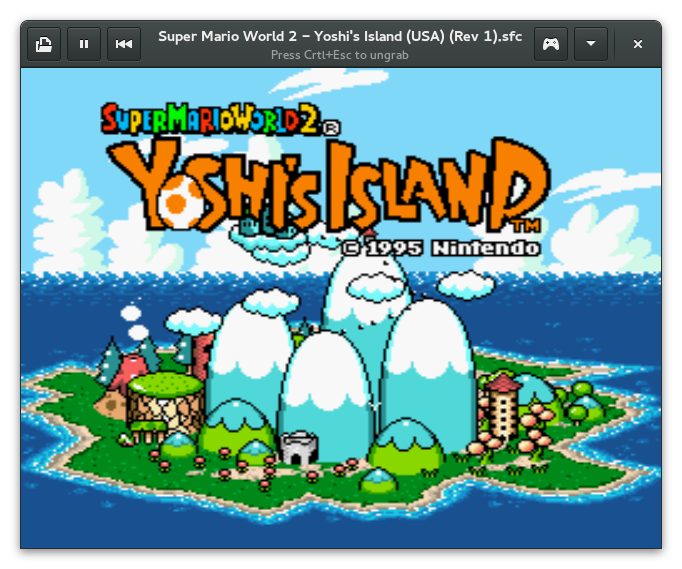
bSNES running Yoshi’s Island, showing the “ungrab the pointer” message
Here is the demo’s git repository: https://github.com/Kekun/retro-gtk-demo
GNOME Games
The ultimate goal of this project is to write a video game manager and player for GNOME, with a user interface similar to GNOME Music or GNOME Video. This project is similar to OpenEmu for MacOS X systems.