Libhandy 0.0.7 just got released! I didn’t blog about this mobile and adaptive oriented GTK widget library since the release of its 0.0.4 version three months ago, so let’s catch up on what has been added since.
List Rows
A common pattern in GNOME applications is lists, which are typically implemented via GtkListBox. More specific patterns arose, where rows have a title at the start, an optional subtitle below it, actions at the end and an icon or some other widget like a radio button as a prefix. These rows can also be expanded to reveal nested rows or anything else that fits the need.
So far every application using these patterns implemented the rows by hand for each and every row. It made using these a bit cumbersome and it led to inconsistencies in sizing, even inside a single application. To make these patterns easier to use, we implemented HdyActionRow, HdyComboRow and HdyExpanderRow.
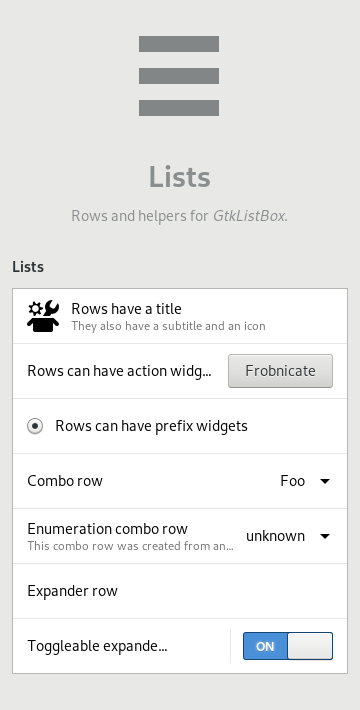
HdyActionRow
The action row is a simple and flexible row, it lets you give it a title, a subtitle, an icon name, action widgets at its end, prefix widgets at its start and other widgets below it. It takes care of the base layout of the row while giving you control over what to do with it.
HdyComboRow
The combo row lets the user pick a single value from a list model, it is quite convenient to use as you can even set it for an enumeration GType.
HdyExpanderRow
The expander row allows you to reveal a widget below the row, like a nested list of options. It lets you optionnaly have a switch triggering whether it is possible to expand the row to access the nested widget or not.
Adaptive Dialog
HdyDialog is a dialog which behaves like a regular GtkDialog on normal conditions, but which automatically adapt its size to the one of its parent window and replace its window decorations by a back button if that parent window is small, e.g. if it is used on a phone. This will mean that HdyDialog will act like a regular dialog on form factors like a desktop, a laptop or a tablet, but it will act like another view of the main window if it is used on a phone or on a really narrow window. HdyDialog has been written by Zander Brown, thanks a lot!
Adaptive Search Bar
HdySearchBar is a reimplementation of GtkSearchBar that allows the search entry to be expanded to take all the available space up. This allows for an expanded HdyColumn between the search entry and the search bar, allowing to automatically adapt the width allocated to the search entry to the one allocated to the bar.
GtkSearchBar from GTK 4 already handles that correctly so HdySearchBar will not be ported to GTK 4.
Internationalization
Libhandy now supports internationalization, there are no end-user-facing strings but developer-facing strings like property descriptions can now be localized.
Initialization
The hdy_init() function has been added, it will initialize the internationalization, the types, and the resources, ensuring Libhandy will work in any context.
Annotation of Symbols Introduction
We started annotating when symbols were added to the API, which will better explain to you via the documentation what is available with your current Libhandy version and which version of Libhandy you should require to use a specific feature.
glade_catalog and introspection Options
The glade_catalog and introspection options have been turned from booleans into features, that means that we broke the build system’s interface as true and false are not valid values anymore and should be replaced by enabled, disabled or auto. Their default value is auto which means that if you don’t care about the availability of these features, you don’t have to care about these options anymore.
Making Libhandy Static
The static boolean option have been added to allow Libhandy to be built as a static library. Note that the introspection and the Glade catalog can’t be built when building Libhandy as a static library.
Bundle Libhandy in a Flatpak Manifest
To bundle the master version of Libhandy in your Flatpak manifest, simply add the following module:
{
"name" : "libhandy",
"buildsystem" : "meson",
"builddir" : true,
"config-opts": [
"-Dexamples=false",
"-Dtests=false"
],
"sources" : [
{
"type" : "git",
"url" : "https://source.puri.sm/Librem5/libhandy.git"
}
]
}
Bundle Libhandy as a Meson Subproject
To use Libhandy 0.0.7 as a Meson subproject, first add Libhandy as a git submodule:
git submodule add https://source.puri.sm/Librem5/libhandy.git subprojects/libhandy
cd subprojects/libhandy
git checkout v0.0.7 # Or any version of your choice.
cd ../..
git add subprojects/libhandy
Then add this to your Meson build system (adapt the package sub-directory name to your needs):
libhandy_dep = dependency('libhandy-0.0', version: '>= 0.0.7', required: false)
if not libhandy_dep.found()
libhandy = subproject(
'libhandy',
install: false,
default_options: [
'examples=false',
'package_subdir=my-project-name',
'tests=false',
]
)
libhandy_dep = libhandy.get_variable('libhandy_dep')
endif
If you don’t require introspection and you don’t care about localization, you can alternatively build it as a static library:
libhandy_dep = dependency('libhandy-0.0', version: '>= 0.0.7', required: false)
if not libhandy_dep.found()
libhandy = subproject(
'libhandy',
install: false,
default_options: [
'examples=false',
'static=true',
'tests=false',
]
)
libhandy_dep = libhandy.get_variable('libhandy_dep')
endif
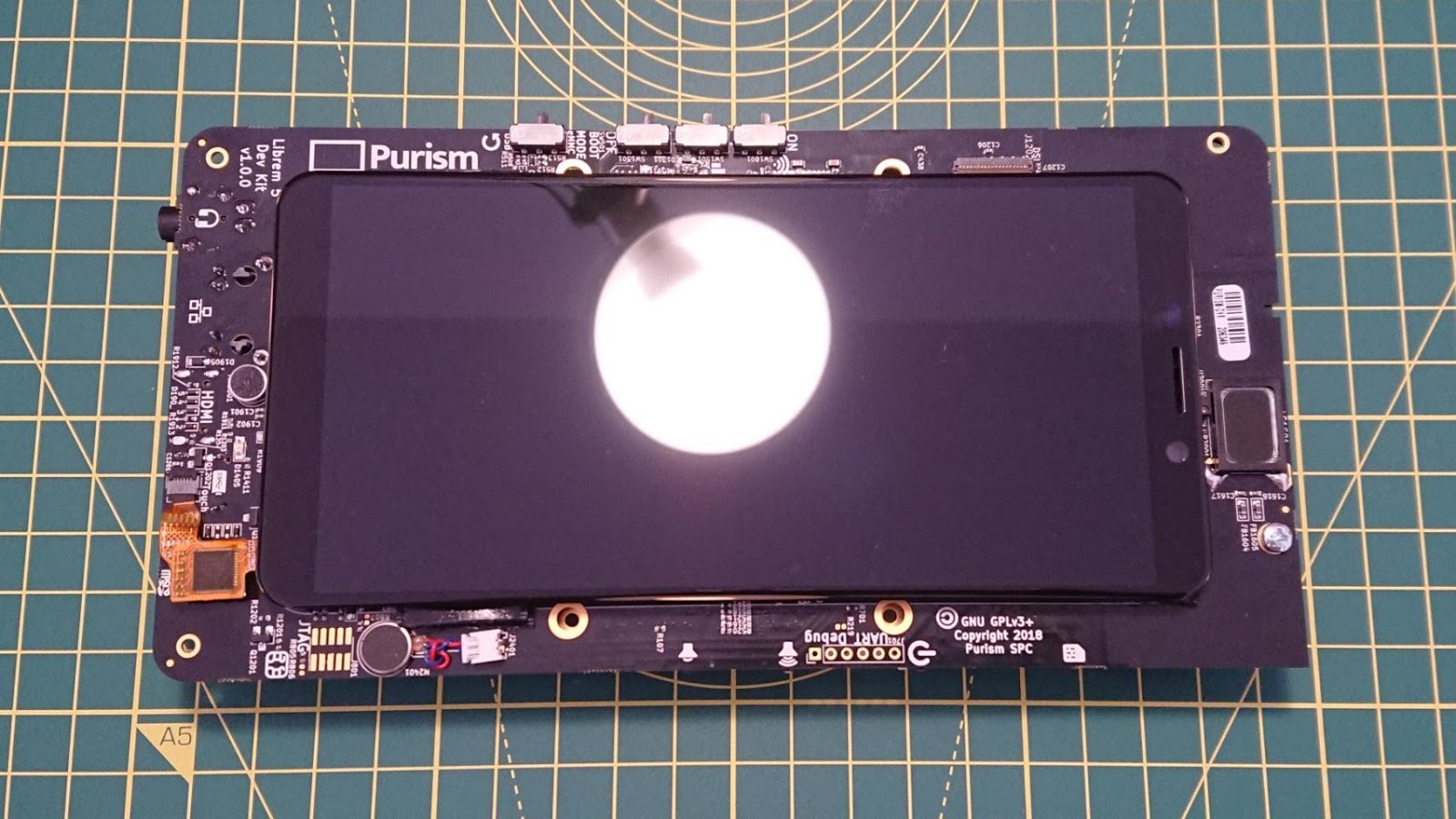
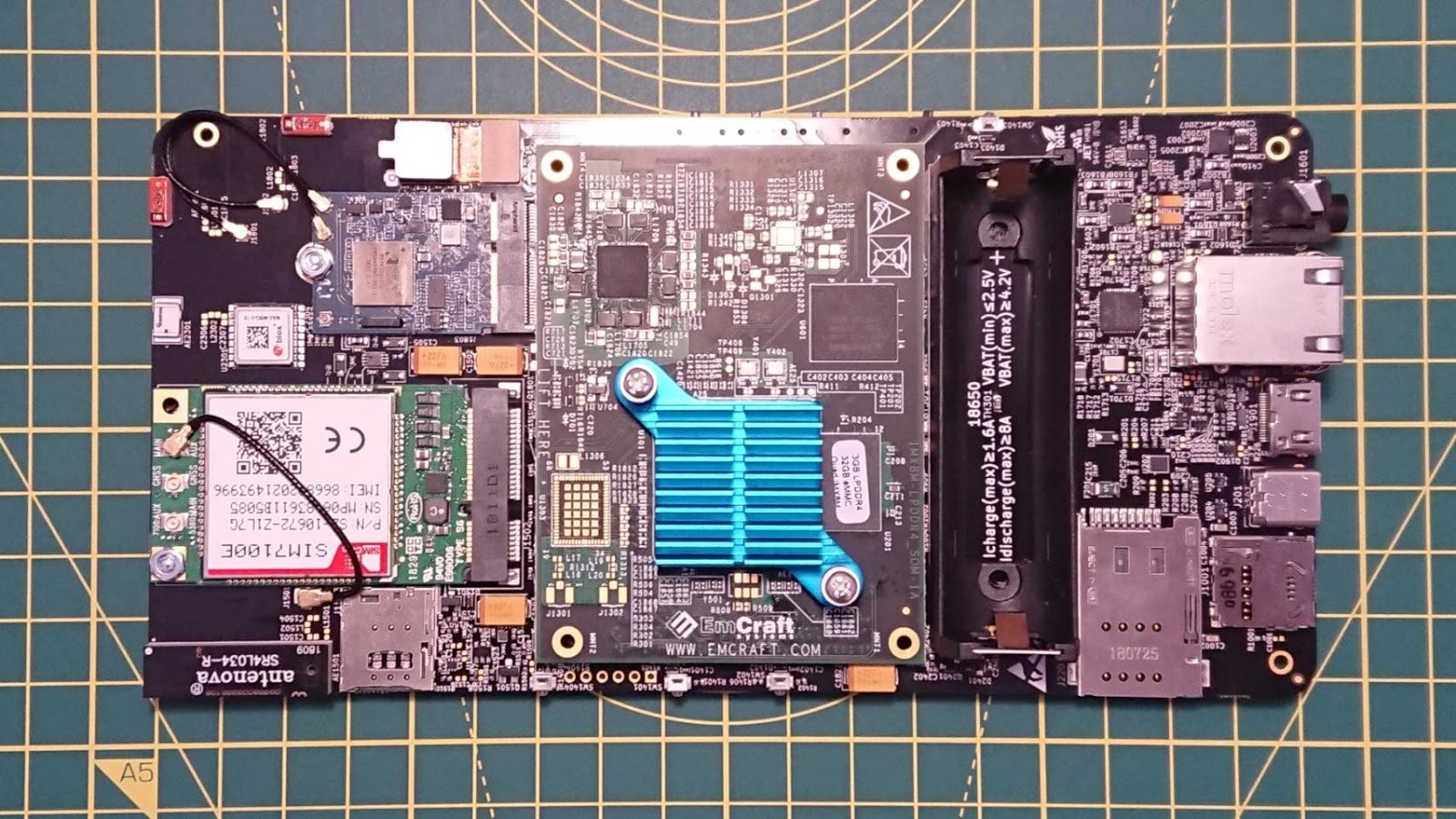
Librem 5 DevKits
As a sidenote: the Librem 5 devkits shipped at the very end of 2018, here are photos of mine! I’m eager to play with Libhandy on it.